Introduction
Insurance provides a method of protecting a person or an entity from a financial loss. Insurance is a form of contingence. It provides hedge, protection from loss, in multiple situations. A company that provides insurance is called an insurance company or an insurer.
Individual insurance his car, house, health, and life through auto insurance, house insurance, health insurance, and life insurance. A company may buy insurance against unforeseen circumstances. They may also insure their equipment and plants.
At the beginning of the insurance industry centuries ago, insurance was simple. People would insurance their lives and companies would insure their products.
But, as new and new industries kept popping up and the needs of humans and companies kept changing, insurance policies also become more complex. Nowadays you can insure almost anything.
You can also insure things that are not yours through a complex set of products called derivatives. These are mainly money-making insurance products and do not provide any real utility.

How does insurance work?
The insurer provides a legal contract to the insured, this contract details the conditions and terms of the contract. It also details the conditions for which the insurance contract would payout.
The insured pays the insurer a premium, a monthly, quarterly, or annual fee, depending upon the timeline specified in the contract. The insurance contract also has a timeline until it expires, it could be five, ten, fifteen, or twenty years and the timeline depends upon the preference of the insurer.
Some insurance terms you need to know to understand how insurance companies make money
There are some terms used in the insurance industry that you need to know if you want to understand how insurance companies make money. These terms and their explanations are given below:
Premiums: Timely payments paid to the insurer by the insured for the insurance contract.
Appraisal: An estimated value of the asset before or after the accident.
Claims: Request for compensation by the insurance holder for payment for the asset damaged which is covered under the insurance contract.
Depreciation: Decrease in value of an asset due to the damage caused to it.
Endorsement: A change in insurance policy to increase, decrease or remove the coverage provided by the insurance contract.
Indemnification: The act of compensating for a loss for the asset covered in the insurance contract.
Lapse: The amount of time for when a person for an asset like a house or a car goes without insurance coverage.
Mitigation: Proper steps taken to reduce the possibility of a loss.
Policy: The insurance contract is called policy.
Title: A legal document showing the ownership of a property or an asset.
How Insurance companies make money
There are four main ways an insurance company makes money. All of these four ways are noted in figure 1 below:
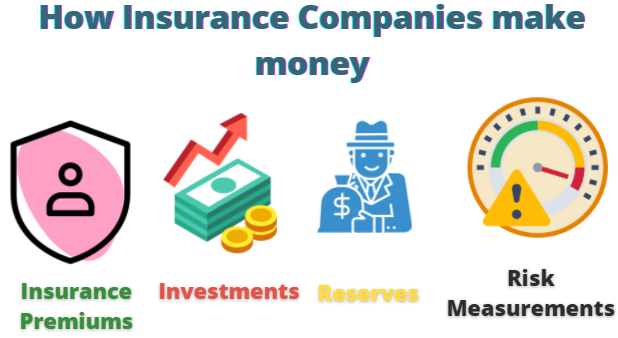
Figure 1:Main ways an insurance company makes company.
The four main ways an insurance company makes money are by the insurance premiums, investing those insurance premiums into investments, reserves, and risk measurements. All four of these methods are explained in great deal below:
Insurance premiums
Insurance premiums are the payments made to the insurer by the insured. The insurance company pools all the premiums of all its customers. This is the main way that an insurance company earns money. Insurance companies are, risk poolers. What this means is that they reduce risk by spreading it.
For example, a company may collect a premium of only ten dollars per month on a life insurance policy from one policyholder which can pay anywhere from one hundred thousand dollars to a million dollars. Now, there is a high risk that this person may die. But, an insurance company may have millions of customers.
The chance is near zero that all of the policyholders die at the same time. So, a few people may die and the insurance company is able to pay them. This is what is meant by risk pooling.
Investments
The insurance premiums collected by the insurance companies are not just alone. They are invested in a number of assets. The percentage depends upon the particular insurance company, but, the insurance companies usually invest in the stock market, government bonds, properties, and some money are left in the bank compounding interest.
The insurance companies have a long investment horizon. The timeline for an insurance company for investment is usually anywhere between ten to twenty-five years.
This is also the amount of time taken by an average life insurance policy to mature. This means a payout of the insurance policy.
Reserves
The reserves of an insurance policy are set through government regulations. Reserves are the amount of capital set apart by the insurance companies to pay for any loss to the policyholder which is covered by the insurance contract.
Reserves also allow an insurance company to avoid any cash flow problem or a financial issue that may arise during an unaccommodating market condition.
Some risk-averse insurance companies also used the metrics created by them to hold extra reserves than those mandated by the government to allow them to better manage risk.
Risk measurements
As stated above, insurance companies are risk poolers. Their main benefit is that they help in avoiding any financial loss that may arise in the future.
The insurance companies help their customers better manage their risks by insuring against these risks. There are various kinds of risks against which an insurance company insures.
These may be personal risks, proprietary risks, or liability risks. The insurance companies accept the risks from the policyholders and that is how they make money. They make money by insuring against risk.
Conclusion
The insurance companies make money by helping their customers protect themselves against any financial loss and in return the customers pay them premiums.
The insurance company invests these premiums to pay to their insurance policyholders for any financial damage they incur against any asset which is covered by the insurance policy.