Key Takeaways:
DuckDuckGO is an online search engine that allows users to search images, videos, news, and music. DuckDuckGo does not show, share or collect any personal information of users. It is very much concerned about user’s privacy.
DuckDuckGo makes it Money through advertising and affiliate revenue, for example, sponsored links. It also gets its Money through affiliate programs with eBay and Amazon and licensing fees for its tracker radar tool. The latest revenue post was in 2020, which was about $100 million when DuckDuckGo had 24 million searches. But today, more than 3 billion searches are performed on DuckDuckGo’s platform every month.
Company Profile:
| Company Name | Duck Duck Go, Inc. © |
| Website | duckduckgo.com |
| Founded- In: | February 29, 2008 |
| Headquarters: | Greater Philadelphia Area, Great Lakes, Northeastern US |
| Founders | Gabriel Weinberg |
| Key People | Zac Pappies (VP), Prakash Swaminathan (VP/Director strategic partnership), Russell Holt (VP, Platform), Jaryd Malbin (Director people Ops), Beah Burger-Lenehan (Director Product), Kamyl Bazbaz (Vice President Communication) |
| Business Model | The online search engine platform |
| Industry | Internet, search engine, privacy |
| Competitive Advantage | Perfect privacy (do not share or collect data), No ads targeting you, and no social engineering techniques based on your searches |
| Revenue | $100 million, 2020 |
| Net worth | $901 million, 2020 |
| Competitors | Startpage, Qwant, Blekko, Gigablast, HotBot, Entireweb, |
What is DuckDuckGo?
DuckDuckGO is an online search engine that allows users to search images, videos, news, and music. DuckDuckGo does not show, share or collect any personal information of users. DuckDuckGo discriminates itself from other search engines by showing all users similar search results for a given search term and not profiling its users.
You can search anything on DuckDuckGo, just like as you search on Google. But DuckDuckgo shows excellent concern on ensuring users’ privacy. Besides, the firm does not record and track its user browsing history and doesn’t log the IP address.

No ads are targeting you because DuckDuckGo does not track or your search history. Additionally, no social engineering techniques were used. In a few instances, the company scrapes content from other search engines such as Bing (but not Google) to give more specific search results. DuckDuckGo is, moreover, integrated with a few third-party platforms like Wikipedia or Apple’s Maps.
A Short History of DuckDuckGo:
DuckDuckGo was founded on February 29, 2008, by Gabriel Weinberg in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania. Weinberg is an entrepreneur who launched Names Database, a now-defunct social network. Initially funded by Weinberg, DuckDuckGo supports advertisements, but the user has the choice to disable ads.
The search engine is basically written in Perl and runs on Linux, Nginx, and FreeBSD. DuckDuckGo is built mainly upon search APIs from several vendors. Because of this, TechCrunch listed the service as a “hybrid” search engine. DuckDuckGo was featured on TechCrunch‘s Elevator Pitch on Friday, 2008, and it was a finalist in the 2008 BOSS Mashable Challenge.
Weinberg began a DuckDuckGo community website (duck. co) in July 2010 to permit the public to report issues, discuss means of spreading the use of the search engine, discuss open sourcing the code, and request features. On February 22, 2011, the company registered the domain name ddg. gg and gained duck.com in December 2018, which was, later on, redirect to duckduckgo.com.
In October 2011, Union Square Ventures and angel investors invested in DuckDuckGo, but before that, DuckDuckGo was self-funded. Besides, Linux Mint, Midori, and Trisquel web browsers switched to use DuckDuckGo as their default search engine.
As of May 2012, the search engine was attracting 1.5 million searches a day. Weinberg reported that in 2011, it had earned US$115,000 in revenue and had three employees and a small number of contractors. In February 2012, Compete.com estimated 266,465 unique visitors to the site. Alexa reported a 3-month growth rate of approximately 51% in April 2011.
DuckDuckGo’s traffic statistics indicate that in August 2012, there were 1,393,644 daily visits, high from an average of 39,406 daily visits in April 2010. In a long-winded profile in November 2012, The Washington Post showed that searches on DuckDuckGo were about 45,000,000 per month in October 2012.
On September 26, 2013, GNOME released Web 3.10, and starting with this version, DuckDuckGO is the default search engine.
On September 18, 2014, Apple announced at its keynote speech at WWDC 2014 that DuckDuckGo would be added as an option for search on both iOS X Yosemite and iOS 8 in its Safari browser. The Pale Moon web browser, which started with version 24.4.0, included DuckDuckGo as its default search engine on March 10 and listed it on its homepage.
DuckDuckGo released a redesigned version in May 2014 to beta testers through DuckDuckHack. DuckDuckGo officially released the redesigned on May 21, 2014. The new version added plenty of new features such as local search, auto-suggest, images, recipes, weather, and more.
On November 10, 2014, Mozilla also added DuckDuckGo as a search option to Firefox 33.1. On May 30, 2016, The Tor Project, Inc added DuckDuckGo, the default search engine for Tor Browser 6.0.
In July 2016, DuckDuckGo officially announced that it extends with Yahoo! that brought the latest features to users of the search engine, including additional site links and date filtering results.
It also partners with Yandex, Wikipedia, and Bing to produce results or make use of features offered. The company also assured that it doesn’t share user information with partner companies, as has always been its policy.
It was reported in December 2018 that Google transferred ownership of the domain name Duck.com to DuckDuckGo. It’s not known what price, if any, DuckDuckGo paid for the domain name.
In January 2019, DuckDuckGo announced that all address-related and map-related searches would be powered by Apple Maps, both on mobile devices and desktop.
In Chrome 73, Google added DuckDuckGo to the default search engine list in March 2019.
Moreover, starting from March 2020, Google was forced to add other search engines within its Android OS. The change was occurred due to a $4.8 billion fine issued by the European Union, which claimed that Google used its Android OS to protect and secure its search dominance.
Because of that fine, Google was forced to surface distinct default search engine options when users set up their Android devices. The choices were decided on a “fourth-price” auction system where search engine operators like Yahoo or Bing would pay for every user signed up via Android.
In September 2020, DuckDuckGo found itself eligible to be selected for four different European countries. The company was simply not able to match the prices its competitors, particularly Yandex or Bing (via Microsoft), we aren’t able to pay.
Despite some of those setbacks, the firm continues to grow significantly. Today, more than 3 billion searches are made every month on DuckDuckGo. The firm, moreover, employs about 300 people – most of them still based in its Paoli headquarters.
How Does DuckDuckGo make Money?
DuckDuckGo makes Money through Affiliate Marketing and Advertising. Advertising is based on the keywords typed into the search box. Affiliate revenues come from eBay and Amazon affiliate programs.
The company collects a small commission when users buy after getting on those sites through DuckDuckGo. It also makes money from licensing fees for its tracker radar tool. DuckDuckGo‘s business model begins from Google’s value proposition.
- Untracked Affiliate Advertising
When a user visits eBay and Amazon through a DuckDuckGo and afterward makes a purchase, DuckDuckGo receives a small commission. This mechanism operates, and there’s no personally identifiable information exchanged between eBay or Amazon, and DuckDuckGo.
- Untracked Advertising
When a users type in a search, DuckDuckGo shows an ad based on that search term. For example, if you type in “boat,” DuckDuckGo shows a boat ad. That does not involve tracking because it’s based on the keyword and not the person.
- Tracker Radar
Launched in March 2020, Tracker Radar is a constantly updated data set about hidden trackers that companies like Facebook or Google employ.
These trackers can choose different data points, including a user’s shopping, location, search history, or browsing. From those, they can infer your gender, interests, age, ethnicity, hobbies, and many other characteristics.
DuckDuckGo’s Tracker Radar provides an overview of the most commonly used trackers and their tracking behavior (i.e., how the cookie behaves or what privacy policy is used.)
This information is publicly available by DuckDuckGo and can be accessed free of charge. However, if someone intends to use it for commercial purposes, a licensing fee must be paid to DuckDuckGo.
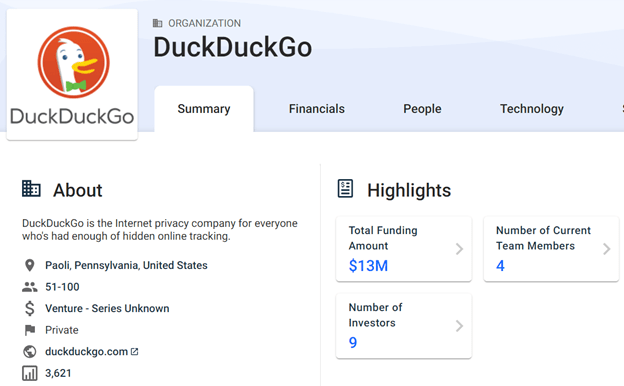
DuckDuckGo Funding, Valuation & Revenue
DuckDuckGo has raised a total of $13 million across two rounds of venture capital funding, according to Crunchbase.
Investors into the company include OMERS Ventures, Union Square Ventures, Joshua Schachter (co-creator of Memepool, amongst others), Scott Banister (founder of IronPort), or Peter Hershberg (co-founder of Reprise Media).
DuckDuckGo is a private company, so it is not obliged to share any revenue or valuation figures. However, in an interview with Philly Mag, CEO Weinberg said that the company generated over $100 million in revenue for 2020.