Key Takeaways:
Charles Schwab Business Model offers small business products and services that one needs to reach their goals. It is a convenient place where you can get business solutions about short-term loans and retirement planning. It is an American transnational money service company that provides a complete range of brokerage, banking, and money informative services through its operative subsidiaries.
The primary operation of Charles Schwab Business is a saving and loan company. It charges some fee when you get engaged in certain activities. It provides you expert commentary timely that helps one to navigate the variation in market conditions. It guides you about the strategies that will help meet your investing needs and will answer all the questions on investors’ minds.
Charles Schwab is a full-service non-depository financial institution with technology that may suit a good variety of investors, from active traders and self-reliant investors who handle their investment to purchasers who are searching for investment recommendation and portfolio management. Futures traders need to open a separate account. However, not like Fidelity, purchasers have access to that asset category.
Company Profile:
| Company Name | Charles Schwab & Co. Inc. © |
| Website | aboutschwab.com |
| Founded- In: | 1971 |
| Headquarters: | Westlake, Texas, U.S. |
| Founder | Charles R. Schwab |
| Key People | Charles R. Schwab (Chairman), and Walter W Bettinger II (President & CEO) |
| Business Model | Public Platform |
| Product/Services | Wealth Management, Stock Brokerage, Commercial banking, Electronic trading platform |
| Competitive Advantage | New ways to deliver, independent advisors, financial evaluation, market opportunity |
| Revenue | $11,691 Million in 2020 |
| Competitors | Legg Mason, Robinhood, Lazard, CITIC Securities, Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs, BlackRock, and TIAA. |
Introduction:
The Charles Schwab Corporation is an American transnational money services company. It offers banking, industrial banking, an electronic trading platform, and wealth management consultative services to each retail and institutional client.
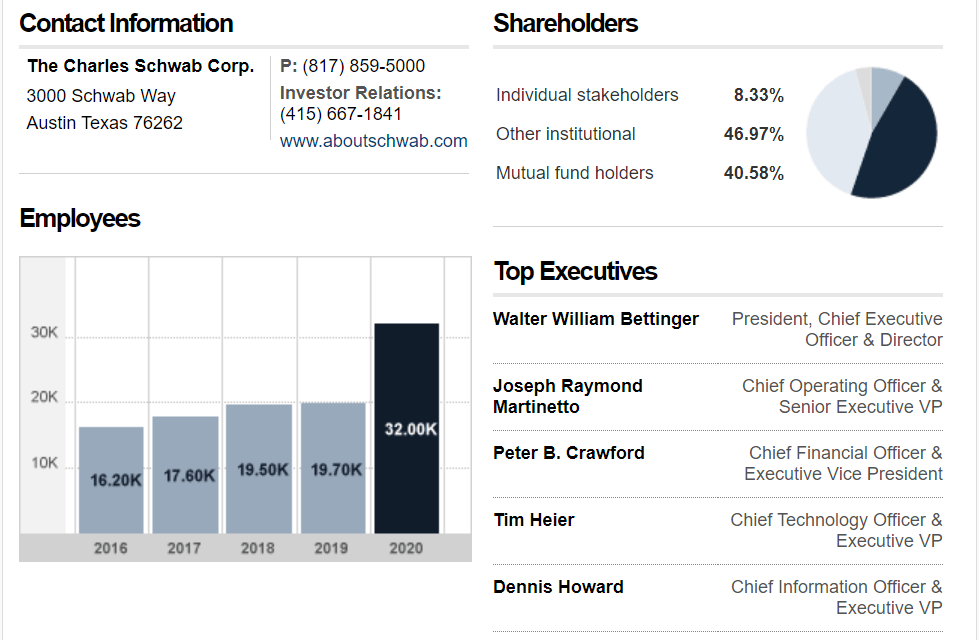
It’s over 360 branches, primarily in money centers within the U. S. and also the U.K. it’s the thirteenth largest banking establishment within the U. S. with over US$3.3 trillion in consumer assets. Behind BlackRock and Vanguard, Charles Schwab Business is the third-largest asset manager with 2.1 million company retirement program participants,$5.9 trillion in consumer assets,1.5 million banking account, and 29.0 million active brokerage accounts as of October 31, 2020.
It was set up in San Francisco, California, and its headquarter was made in 1971 in Westlake, Texas, and founded as Charles Schwab & Co. by its namesake Charles R. Schwab. The company capitalized on the financial liberation of the seventies to pioneer discount sales of valuation securities.
After a flagship starts in Sacramento, the bank enlarged into an urban center before the Nineteen Eighties economic growth supported its investments in technology, automation, and digital record keeping. Bank of America originally purchased the primary to supply round-clock order entry and quotation in 1983 for $55 million. Three years later, the bank’s no-charge mutual funds’ profitableness prompted the founder to shop for his company back for $280 million.
What is Charles Schwab Business Model?
The Charles Schwab Corporation provides a complete range of brokerage, banking, and money informative services through its operative subsidiaries. Its dealer subsidiary, Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. (Member SIPC), offers investment products and services and Schwab brokerage accounts. Its banking subsidiary, Charles Schwab Bank, SSB (member Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and an Equal Housing Lender), provides deposit and disposal services and products. Access to Electronic Services could also be restricted or out of stock in periods of peak demand, market volatility, systems upgrade, maintenance, or alternative reasons.
Charles Schwab Business Model is rated as one of our most outstanding brokers for ETFs and ETF screeners. There is a wide array of tools and services designed to charm all or any investment levels. The Mobile internet platforms and native mobile apps are featured because of the desktop expertise. Customers should take action to extend their returns on uninvested money.
On November 25, 2019, Charles Schwab declared it’d acquire T.D. Ameritrade’s online brokerage. In August 2020, Schwab confirmed that T.D. Ameritrade’s suppose or swim platform can carry on when the acquisition is complete.
A Short History of Charles Schwab Business Model:
For over forty years, The Charles Schwab Corporation has been an advocate for individual investors and the money professionals who serve them.
In 1963, Charles R. Schwab and two different partners launched Investment Indicator, an investment newsletter. The newsletter had 3000 subscribers at its height, every paying $84 a year to subscribe. In Apr 1971, the firm was incorporated in California as 1st Commander Corporation, a completely in hand subsidiary of Commander Industries, Inc., for ancient brokerage services and to publish the Schwab investment account. In Nov of that year, Schwab and four others bought all the stock from Commander Industries, Inc., and in 1972, Schwab purchased all the stock from what was once Commander Industries. In 1973, the corporate changed its name to Charles Schwab & Co., Inc.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission provided permission for negotiated commission rates in 1975, and Schwab got wind of a stock brokerage. In Sep 1975, Schwab opened its 1st branch in the state capital, C.A., and began giving discount brokerage services. In 1977, Schwab started giving seminars to purchasers, and by 1978, Schwab had 45,000 consumer accounts total, doubled in 1979 to 84,000.
In 1979, Schwab put at risk $500,000 for a back-office settlement system called BETA (which was short for Brokerage Execution and dealings Analysis), enabling Schwab to become the primary discount broker to bring automation in-house. In 1980, Schwab established the industry’s 1st 24-hour quotation service, and therefore the total of consumer accounts grew to 147,000.
And thus, in 1981, Schwab became a member of the stock market, and therefore the total of consumer accounts increased to 222,000. In 1982, Schwab became the primary to supply 24/7 order entry and quote service, its 1st international workplace was opened in Hong Kong, and therefore the range of consumer accounts totaled 374,000.
In 1983 Bank of America acquired the firm for $55 million. Schwab then introduced the new Schwab One brokerage account. In 1984 Schwab introduced Mutual Fund Market Place with 140 no-load funds. The company launched Schwab Quotes and introduced The Equalizer, a DOS-based technology solution that pointed toward an online future. In 1985 August, Schwab recorded its 1-millionth client account. By year’s end, client accounts reached 1.2 million with client assets of $7.6 billion. In 1986 Schwab became the first to allow clients to place mutual fund buy or sell orders 24/7.
In 1987, management and Charles R. Schwab bought the corporate from Bank of America for $280 million. In 1991, the corporate noninheritable Mayer & Schweitzer, a market-creating firm, permitting Schwab to execute its customers’ orders while not sending them to associate exchange. It was fined $200,000 for failure to rearrange the most effective trades for its clients in 1997. In 2000 the unit was renamed Schwab Capital Markets. In 1993, the corporate opened an associate workplace in London.
In 1995, the corporate acquired The Hampton Company, supported by Walter W. Bettinger, who became chief executive officer of Schwab in 2008. In 1996, web commerce went live. Customers will trade listed and over-the-counter stocks, check balances, and the status of orders on the schwab.com website. In 1998, discontent by the in-house results, the corporate employed interactive firm Razorfish to revamp the online website. Years later, the website would be entered within the Cooper-Hewitt Museum’s inaugural National style Triennial.
Schwab bought U.S. Trust for $2.73 billion in 2000, and in 2001, less than a year after the purchase of U.S. Trust, the U.S. Trust subsidiary was punished $10 million during a bank secrecy law case. It was ordered to pay $5 million to the New York State Banking Department and $5 million to the Fed Board. On November 20, 2006, Schwab declared an agreement to sell U.S. Trust to Bank of America for $3.3 billion in money. The deal enclosed the second quarter of 2007.
In Jan 2004, Schwab acquired SoundView Technology group for $345 million to feature equity analysis capabilities. David S. Pottruck shared the chief operating officer title with the founder of the company from 1998 to 2003. In May 2003, Mr. Schwab left and gave Pottruck sole control as chief operating officer. On July 24, 2004, the company’s board suspended Pottruck and replaced him with its founder and namesake.
News of Pottruck’s removal came because the firm had proclaimed that overall profit had born 10 percent, to $113 million, for the second quarter, driven mainly by a 26th decline in revenue from client stock trading.
After returning to management, Mr. Schwab additionally rolled back Pottruck’s fee hikes. The corporate rebounded, and earnings began to show around in 2005, as did the stock. The share value was up as high as 151% since Pottruck’s removal, ten times since Charles Schwab’s come. The company’s net transfer assets, or the assets that return from alternative companies, quadrupled from 2004 to 2008.
Schwab’s YieldPlus fund drew controversy throughout the 2007 financial crisis due to its -31.7% return. Investors within the Schwab YieldPlus Fund, together with Charles Schwab himself, lost $1.1 billion. Schwab closed the YieldPlus funds in 2011. In April 2007, the corporate acquired the 401(k) Company.
On July 22, 2008, Walter W. Bettinger was named chief executive, succeeding the company’s namesake. In 2011, the corporate acquired Options Xpress. The corporate additionally acquired Compliance11, Inc., a supplier of the compliance software system.
In 2012, it acquired Thomas Partners, a quality management firm. On July 1, 2020, the corporate acquired Wasmer, Schroeder & Company, an independent investment manager of mounted financial gain in individually managed accounts with $10.7 billion in assets under management.
On May 26, 2020, the corporate acquired USAA’s investment management accounts for $1.8 billion in money. In June 2020, the corporate began permitting investors to get fractional shares. On October 6, 2020, the corporate completed the acquisition of T.D. Ameritrade. On January 1, 2021, the corporate moved its headquarters to Westlake, Texas.
What is the Business Model of Charles Schwab Business?
Charles Schwab operates primarily as a savings and loan company. Its subsidiaries are engaged in wealth management, securities brokerage, banking, cash management, and financial consultative services.
The operations of the company are divided into two business segments: investor Services that comprises of the provision of the company of retail brokerage and banking services, retirement savings plan services, and different company brokerage services; and authority Services, consisting of the company’s provision of guardian, trading, and support services, also as retirement business services.
How Does Charles Schwab Business Make Money?
Schwab charges a fee after you engage in certain activities in your accounts. The fee doesn’t vary whether or not you receive a recommendation from us. On rare occasions, fees are waived, discounted, or negotiated supported assets or alternative business criteria. Additionally to the fees, the investments suggest having prices reflected within the worth of the product. These vary by investment.
Charles Schwab’s key resources area unit its money resources, its technology, and communications infrastructure – as well as it is mobile and online platforms, its sales and distribution channels, its physical branch network, its personnel, and its partnerships.
Charles Schwab Business Funding, Valuation & Revenue:
Charles Schwab incurs prices in relevance the operation and maintenance of its technology and communications infrastructure, the operation of its sales and promoting channels, the management of its partnerships, the implementation of promoting and advertising campaigns, the payment of skilled fees, and use of vendor services, and also the retention of its personnel.
In 2015 Charles Schwab accumulated prices in relevance to the payment of compensation and advantages to the company’s 15,300 staff within $2.24 billion. The company’s professional services fees totaled $459 million for the year, its occupancy and equipment prices amounted to $353 million, and its market development and advertisement development prices were $249 million.
Charles Schwab makes revenue through its provision of various banking and non-banking financial services, together with investment consultative, trading, retail brokerage, and plan services of retirement. The company’s revenue is derived from commission and administrative fees related to these services, increased interest, and commerce activities. In 2015 an annual net revenue, Charles Schwab generated $6.38 billion, up marginally on the $6.06 billion recorded by the corporate within the previous year.
The gathering of asset management and administration fees accounted for 41st of the company’s 2015 revenue, with trading revenue representing July 14. Net interest attained accounted for 400th of total revenue, with the remaining revenue created up by the company’s different business operations that don’t work into the activities of the company’s two core business segments.